Rules For Ray Diagrams









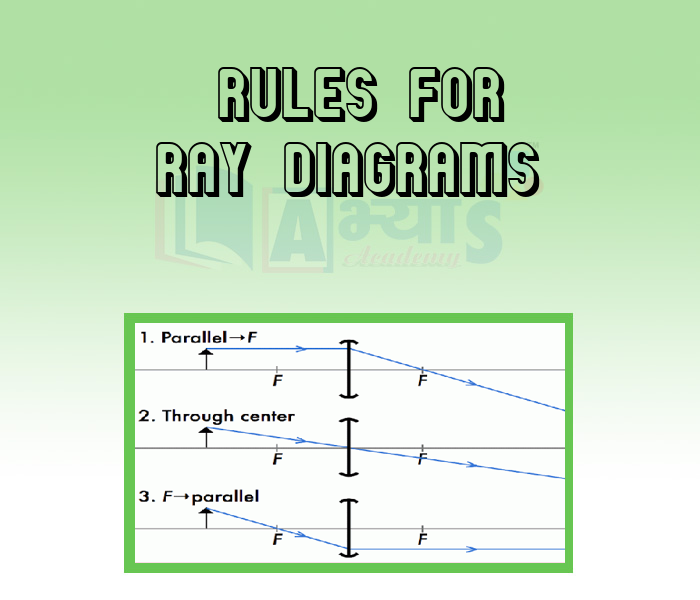
Rules For Ray Diagrams
Representation of Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors Using Ray Diagrams:
Many rays of light are coming from the point object or an extended object in all directions.The reflection of light follows the same two rules for all rays. The image of the object is formed at the intersection of the reflected rays To construct a ray diagram in order to locate the image of an object, it is more convenient to consider only two rays. The intersection of at least two reflected rays gives the position of image of the point object.
The following rays can be considered for locating the image
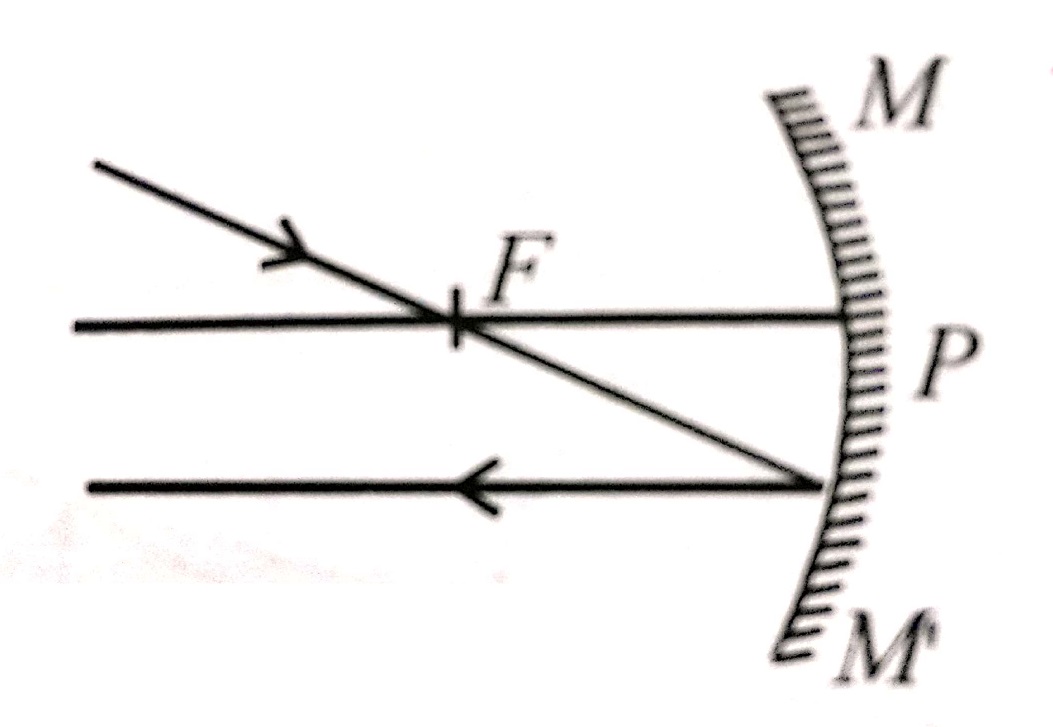
1.The rays coming parallel to the principal axis, pass through the focus after reflection in concave mirror or appear to come from focus in the case of convex mirror.
 |
 |
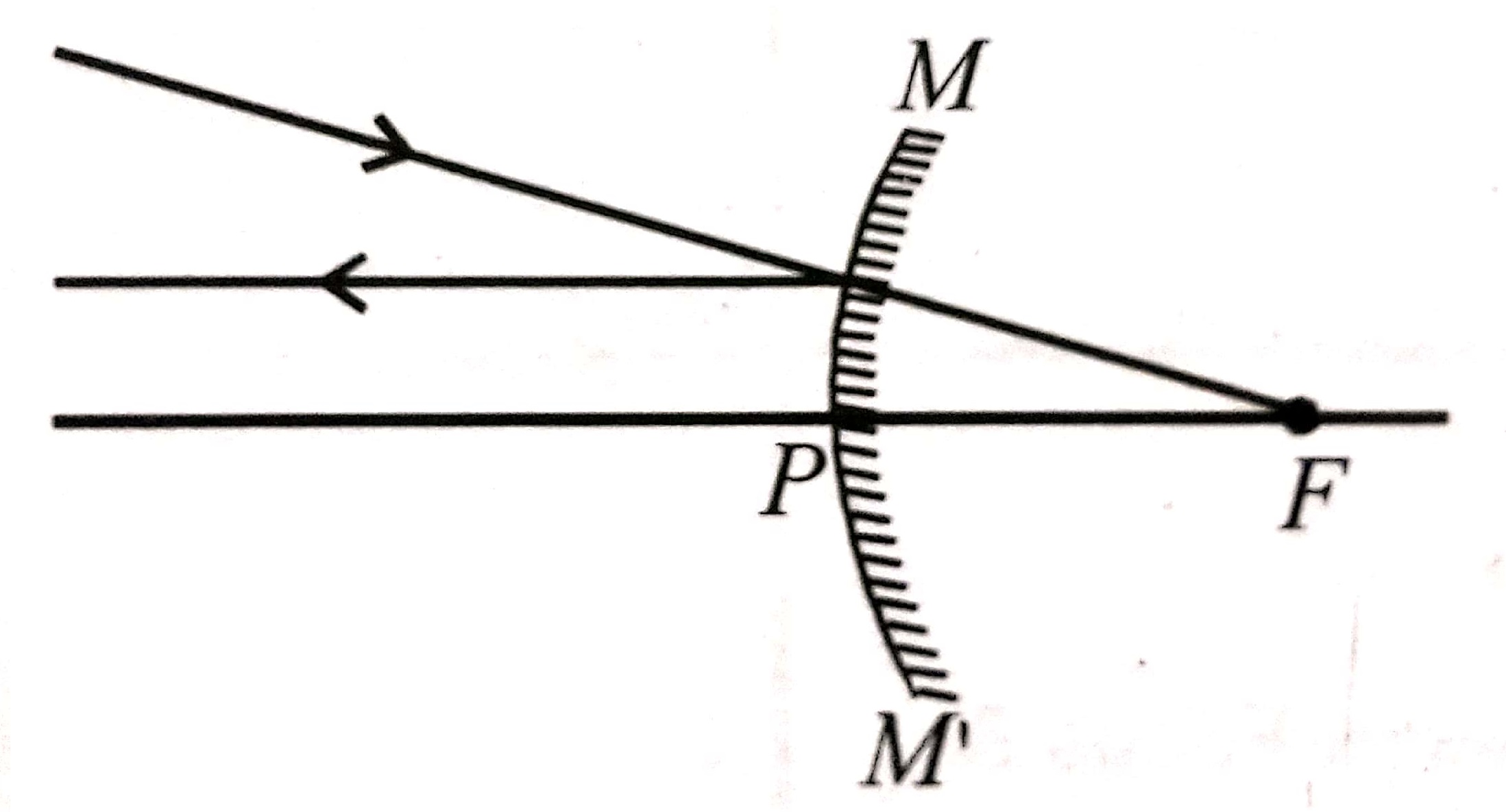
2. The rays coming through the focus of a concave mirror or coming towards focus of a convex mirror, become parallel to principal axis after reflection from the mirror.
 |
 |
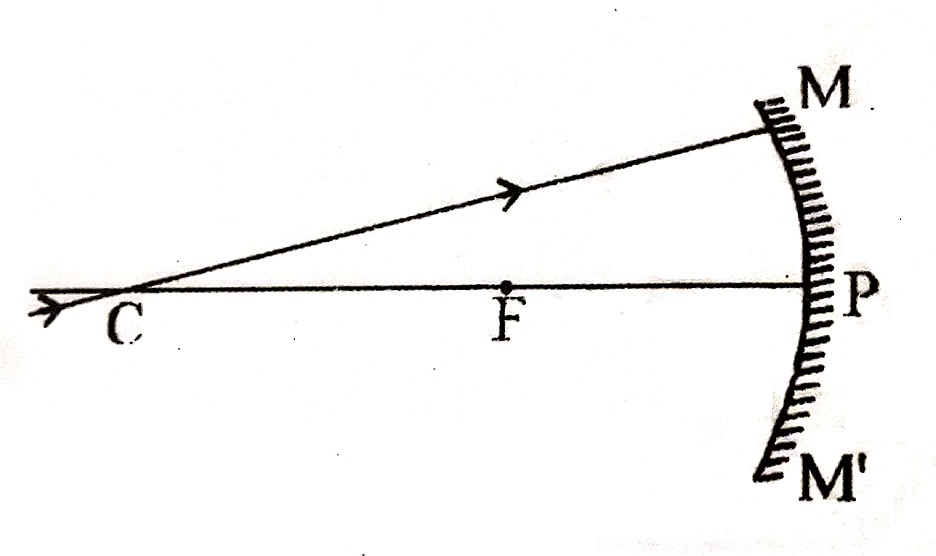
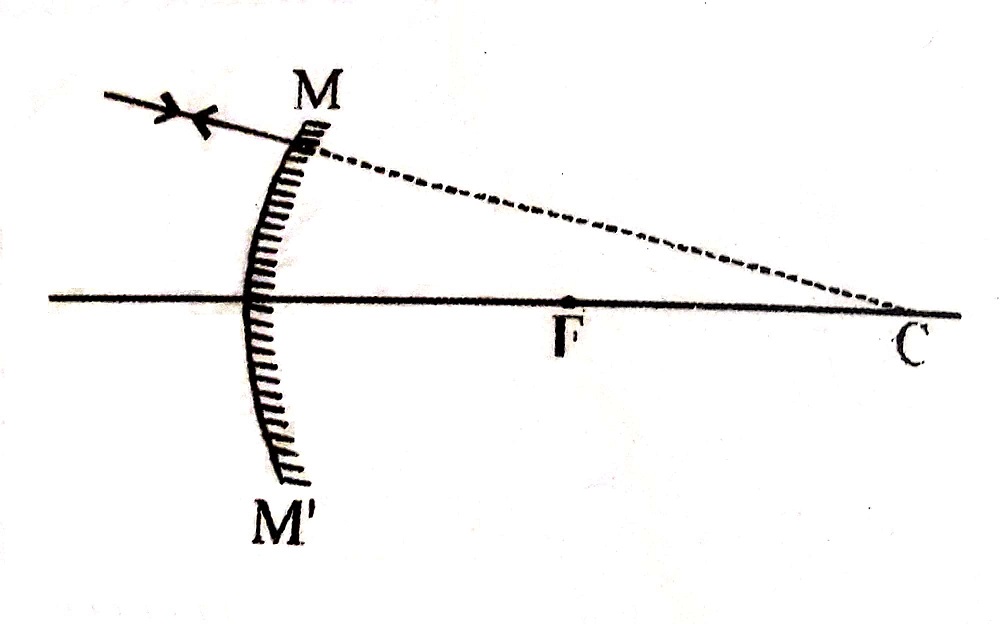
3. A ray coming through centre of curvature of a concave mirror or towards the direction of centre of curvature of a convex mirror, reflects back along the same path on striking the mirror surface.
 |
 |
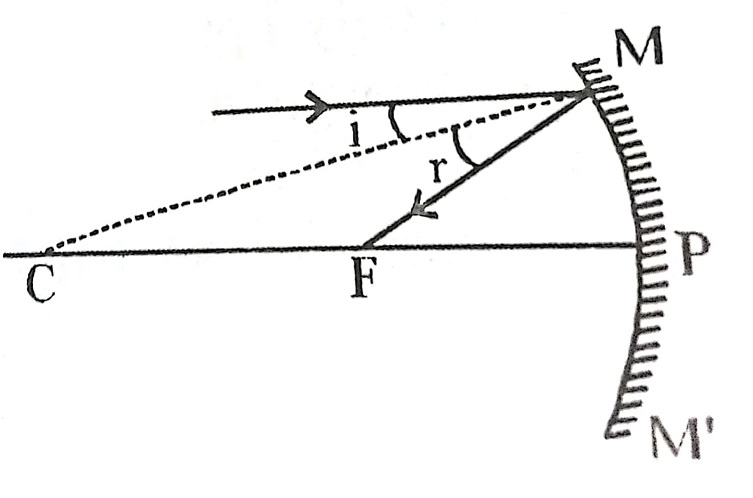
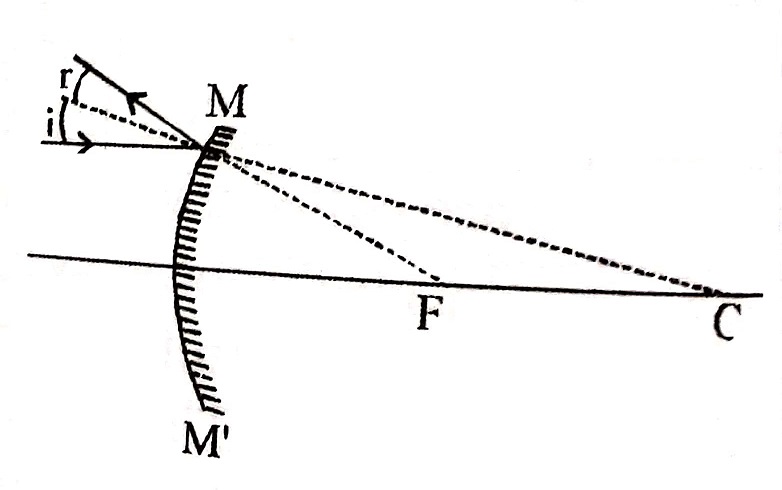
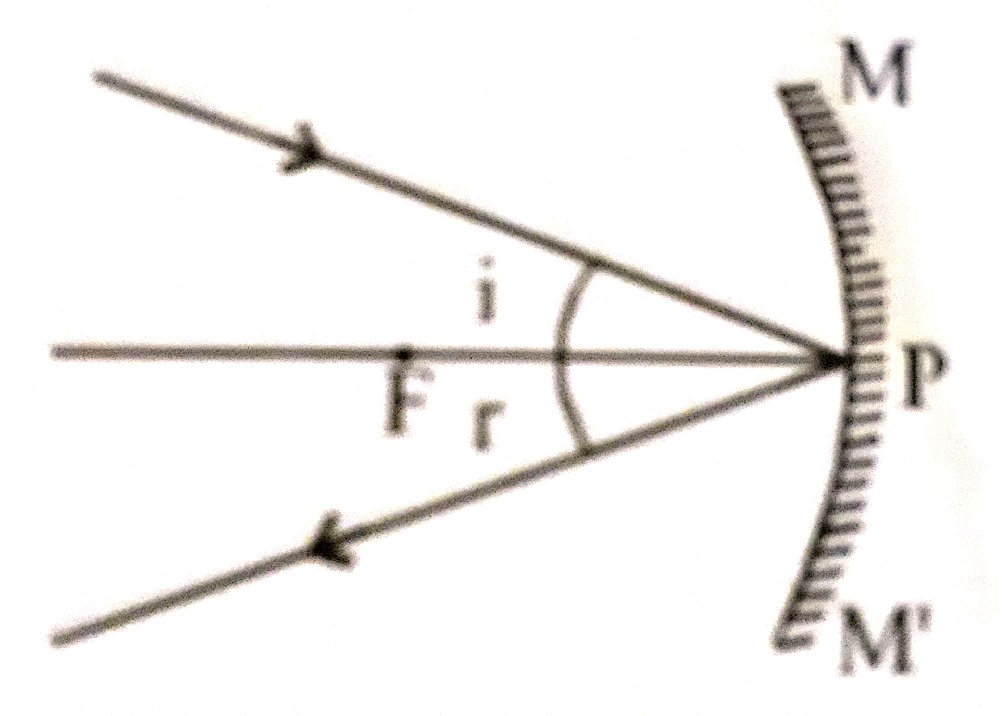
4. A ray incident obliquely to principal axis towards a pole P of the concave or convex mirror is reflected obliquely , following the laws of reflection. i.e., <i = <r.
 |
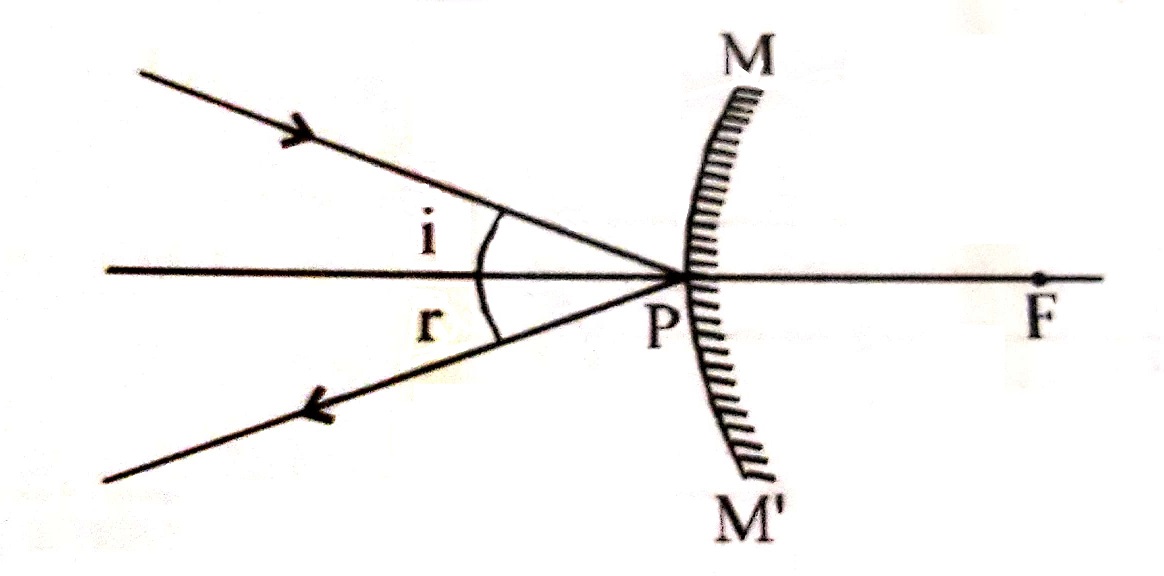 |
Point Object On the Principal Axis:
When the point source is placed at the principal axis of a spherical mirror. The ray along the principal axis will fall normally on the mirror and will retrace its path after reflection. Any other ray which will fall on the mirror will be reflected back (after projection) will cut the principal axis. The image of the point source is formed at that point on the principal axis.
Extended Object Placed Perpendicularly On the Principal Axis:
When the extended object is placed perpendicularly at the principal axis of a spherical mirror, the image of the extended object can be formed by locating the images of the individual point of the object. We can find the whole image by just locating the image of the top and the bottom of the object.
The ray along the principal axis will fall normally on the mirror and will retrace its path after reflection. Any other ray which will fall on the mirror will be reflected back (after projection) will cut the principal axis. The image of the point source is formed at that point on the principal axis.
Which of the following are correct : (a) The rays coming parallel to the principal axis, pass through the focus after reflection in concave mirror. (b) The rays coming through the focus of a concave mirror or coming towards focus of a convex mirror, become parallel to principal axis after reflection from the mirror. (c) A ray coming through centre of curvature of a concave mirror, reflects back along the same path on striking the mirror surface. | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following are correct : (a) Many rays of light are coming from the point object or an extended object in all directions. (b) The image of the object is formed at the intersection of the reflected rays. (c) The intersection of at least two reflected rays gives the position of image of the point object. | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
The rays coming _________________ to the principal axis, pass through the focus after reflection in concave mirror or appear to come from focus in the case of convex mirror. | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
I have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice
